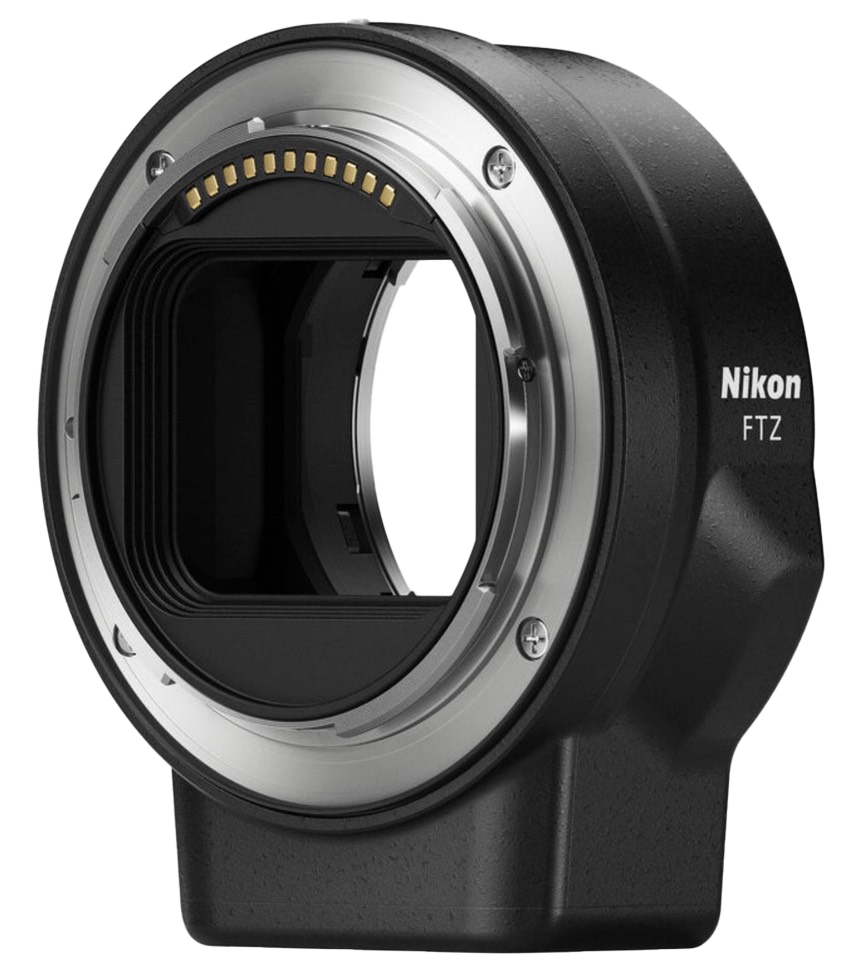
Nikon has so far made two variations of their FTZ adapter in order to be able to use ‘F’ mount lenses on their ‘Z’ mount mirrorless system. The first version had an ugly tripod foot which embarrassingly got in the way with the Z9 body when they eventually released the camera; it was not very well thought out. The second, improved this design, shaving off the foot completely and giving the adapter a closer to round appearance. (Note, it is not perfectly round, there is a lump on it’s side to house the aperture motor for AF-S lenses. This is annoying because collars etc cannot be added to mount heavy lenses, and they could have simply made a rotatable, removable foot. It seems like these things were rushed products, with the B team working on them). The aperture motor works with AF-S, AF-I, AF-D, and AF lenses, as well as manual focus lenses with an ID chip like Nikon AI-P, Voigtlander SL, and the Zeiss ZF.2, Milvus, and Otus lines. It even works with AI-S lenses if someone adds a "dandelion" chip to the lens. Despite these two previous adapters, many Nikon diehards are still waiting on an FTZIII which would autofocus all lenses Nikon has made since the 1980s which have screw-driven autofocus. Most of these are AF-D lenses (the terminology was such that these autofocused (AF), and provided distance information (D) to the camera so that automatic flash exposure could be properly calculated). These types of lenses came on the scene in early 1980, and generally speaking most are better built than the AF-S G lenses in my opinion. (Remember, there are AF-S D lenses from the later end of their production). Screw driven autofocus lenses are lenses which do not have a focus motor within the body of the lens, and rely on the motor residing in the DSLR camera to physically connect into the lens and move the focusing block within it. AF-S, AF-I, and AF-P lenses all have focus motors intrinsic to the lens.
I assume Nikon considered the potential reduced revenue from sales of Z mount lenses and decided not to develop a proper, all bells and whistles adapter for the market. I think this has been a rather foolish and short sighted strategy from a company that, around the time of the D850, made presentation after presentation about their heritage and how they believed new technologies could combine with old to provide great cameras, and technological solutions. I believe they lost a lot of people who were then free to explore Sony or Canon mirrorless systems, as they’d have to buy a lot of new lenses that they where using on the DSLR bodies anyway if they wanted their full functionality. People are still talking about this years later, and the fact they have not done this so far has only hurt their reputation. Nikon have truly failed to understand the sort of added value something as simple as this could give their brand. It’s not always about making huge volumes of money on each product (although I do think if this was done correctly they could easily make a profit off it. Just simply sell it as the new adapter that does everything and bin the other two - consolidate them.). For me, it’s about creating an unmatched brand value and system that is unrivaled in it’s backwards compatibility. Nikon should not underestimate brand cohesiveness and the message that sends to the loyal fanbase who have been using their camera’s and lenses for decades.
The Rumours Have Started
A new rumour has surfaced via China that Nikon has a working FTZ adapter tested previously, yet never released. Apparently Nikon are gearing up to release this adapter in 2025. This has been further reported by the reputable NikonRumors website, with them stating the obvious about the facts of the matter so far. The chatter on this problem has never stopped from day one. On release of the Z mount system of cameras and lenses there was a large resounding ‘Boooo’ from many Nikon die hards who were not interested in buying new lenses when they already had collection they were happy using already. This noise has remained, and the initial disquiet was similar to the single card slot thing that made Nikon bring out version II of their Z6/Z7 cameras. They have done the same thing with these adapters; and to me it seems they are slow at learning these things, or the bean counters should be tied up in a dark room and left to mull over their bad decisions for a few weeks with only bread and water.
There is also a second rumour, via a contact that I have through another. They are apparently, usually quite reliable. The scoop is that there is an adapter which is fully tested and ready to go. We don’t know much more than this, and the reality is that Nikon like any large company could decide to pull this at any minute. If this is all true, I really, really hope they don’t do this, and I think it is unlikely that they would do so if they had come this far with the project already. So, this could be quite an exciting year for Nikon in 2025. The added value they would bring to their F and Z mount systems stretching back decades would be simply immeasurable.
Nikon have a history of deep legacy support and a long, rich heritage…and they never stop telling us about it whenever they get the chance. It boggles my mind that they don’t just flesh one out (I’ll bet, as mentioned that they have a prototype of this already) and add huge value to their system and get some excellent far reaching publicity on the internet while at it. (While you are at it Nikon - you need to address the firmware inconsistency across your lineup of Z mount cameras. Most don’t even have 5:4 crop mode in them, and some are missing functions other cheaper cameras have - edit: this needs to be another article I think).
Some Thoughts
This is certainly not a difficult engineering problem for any competent engineer, less the team of designers at Nikon. I think this has been more about the bean-counters than anything else. There is no doubt in my mind that the type of adapter sought is absolutely viable. There are some areas of consideration:
The proposed adapter has been postulated to draw more power - however I don’t see any reason why. Realistically, the onboard autofocus motors in the Z lenses (or AF-S lenses via the FTZII) draw a power from the battery. It would matter little where that power was used; either in a lens based motor, or an adapter based motor. The current FTZII is already communicating power from the camera battery via it and into the lens. Nothing really changes here.
The adapter would need to be engineered to understand the protocols coming out of the AF-D lenses and be able to accurately do their autofocus ‘stuff’.
Retaining weather sealing would be nice as per the current designs, this could simply be considered and brought over to the new adapter.
Ignore what posters on prominent photography forums say about this for the most part. They are obsessed with ‘new is better’. They are blinded by it. Forums are full of gear heads that couldn’t shoot a competent picture if they tried. It’s the ‘all the gear no idea’ thing going on with most of these fora, for the most part at least. I’ve noticed that our profession is littered with people that think a new camera or lens will solve a problem; or make them better. The marketing is all geared to play to this internal self doubt they have. You aren’t a man if you don’t shoot the latest 45MP camera! There even seems to be this misplaced animosity toward people still wanting to use some old glass, or use older lenses for specialist shooting purposes as I do. Such is the strangeness of these types of places which are full of negativity and over moderation, such that rational thought cannot properly win-out. Why does it bother these people so much if they would not actually use the proposed adapter if produced? Looking at the evidence I am seeing; it seems to get them easily bent out of shape. Amusing? Yes. Sad? Yes.
I think Nikon should have brought out the adapter expected of them from day one. Nikon’s initial adapter and even it’s second, are by far the worse out of the three big players. They simply have been outclassed here and they should be embarrassed about this. I am acutely aware that Nikon have stopped physically producing most of the lenses that this adapter would / could be used for, however that never stopped Sony from doing something very similar, and absolutely does not displace the added brand value it would bring along to the Nikon ecosystem. They also aren’t making any new AF-S, G, P, or I lenses either, yet it still works for those.
Consider that if the adapter made zero profits for Nikon, it really could be thought of a ‘Halo’ product. Ford lost money on the Mustang for three decades. However, they knew by having it in movies, in showrooms etc that it would sell other products. It was cool to buy and own a Ford car. There are many examples of this in industry. Nikon need to think about this on a deeper level, especially when they are so used to harping on about brand heritage and backwards compatibility! I still argue they have done this back to front, however they have now fleshed out most of the Z mount. Now, finally is the time to do right and stand by your own company ethos.
What is even more ridiculous on Nikon’s part on this whole manual focus farce on mirrorless with the AF-D lenses, is that the Zf body Nikon released a good while ago now came out with a very useful function known as ‘manual focus eye detection’. This allowed a shooter using manual focus glass (or AF-D glass which has been crippled on the FTZII by Nikon) to detect the eye, thus on a button push we get a magnified view and can focus the lens easily. This is a huge boon, and makes manual focus much more efficient. Has Nikon bothered to put this into their flagship bodies all this time since the Zf release? No, they haven’t…
Sony LA-EA5
And guess what. Sony have already done this more than four years ago. Sony used to have DSLRs before they became market leaders in the mirrorless world. Their DSLR, ‘A’ mount, lenses, can be mounted to their ‘E’ mount mirrorless cameras with this adapter. It has support for A mount lenses similar to Nikon’s, which do not have the autofocus motor onboard the lens. They even let advanced functions like eye autofocus be used on certain cameras, and support up to 11 FPS! It’s also noted that Sony’s version works screw driven lenses about as fast as their DSLRs do. The facts are simple: Nikon are just way behind Sony in this metric, they have been simply out classed. Despite having both aperture and focus motors, Sony’s is the same price as Nikon's adapter with just an aperture motor. It's also perfectly cylindrical, instead of having a bump for the aperture motor like Nikon. It is a vastly superior design on many counts. This is Sony’s third adapter. The LA-EA3 didn’t support screw drive autofocus. The LA-EA4 did, but had pretty poor autofocus. Another adapter from Nikon now, would be their third…
Nikon Greatly Overexaggerate
Have a look at this, from here: https://backcountrygallery.com/exclusive-nikkor-90th-anniversary-interview/
"- Is there a technical limitation that prevents a focus motor in an FTZ adapter, and if not, would you consider adding that to a future version to drive older F-mount autofocus lenses?
(Ishigami)
In order to provide such support, we would need to design an FTZ with a built-in motor, which would, for the sole purpose of AF-D compatibility, require a considerable increase in the size and mass of the adapter. To be completely honest, this is not our highest priority.
We are devoting our development resources on expanding the Z mount system and maximizing its benefits. This is not to say that system compatibility is not important—of course, I know that there is demand from the market, I would appreciate it if you could understand our reasoning."
This is just complete codswallop. Let’s examine this a little closer. There is simply no reason that the adapter would require to be "considerably" larger. Sony's adapter already weighs less than Nikon's does - The LE-LA5 weighs 88g vs the FTZ-II at 135g, so Sony figured out how to make an adapter with a focus motor that is lighter and is smaller than an FTZ-II without a focus motor. The Sony is also a polished and refined design: it's nicely round with no protrusion for the aperture motor like the FTZ has, and it's lighter. Nikon have absolutely been outclassed here in this respect with these FTZ's, there are no two ways about it...
Regarding their statement that it is not their priority; that is their prerogative. Despite this, the demand for one still exists, and by not meeting it, just makes them look bad.
Items that could be in a FTZIII
Autofocus support for all G and D type screw-drive lenses (again, this is mainly AF-D lenses)
Full AI lens support. Nikon AI lenses are manual focus and decades old, however Nikon went real lazy here. They only meter in two modes, and they don’t even record the shooting aperture on the FTZI or II in the EXIF. That’s not really difficult to do Nikon, come on…
Removeable tripod foot. I stated the foot either on the FTZI which was later removed in the II. It might be nice to have the option, as per the Sony LA-EA5 adapter
Rotating Tripod Collar. Really useful for vertical shots when using an adapter
Some Favourite Classic Lenses
Top of the list is the 85mm f/1.4D which I’ve previously written about here. Then there is the 135mm f/2D. Then let’s consider this other fairly large list, there are many more than this though:
20/2.8D
24/2.8D
28/2.8D
28-70/2.8D
28-105/3.5-4.5D
35/2D
35-105/D
50/1.4D
50/1.8D
60/2.8D macro
70-180/D macro
85/1.8D
85/1.4D
105/f2.5 AI
105/2.5 AIS
105/2D
135/2D
180/2.8D
200/4 macro
300/4D
It’s not a short list, and this doesn’t even nearly list all of them that could be brought into full compatibility with Z mount. Why you ask? Is a picture needed? Ok, let’s go modern classic: